Pneumatic compression devices represent a significant advancement in therapeutic technologies, offering a non-invasive approach to manage various circulatory and lymphatic conditions. These devices utilize controlled air pressure to enhance blood flow and lymphatic drainage, thereby reducing edema and improving overall circulation. Understanding their mechanisms of action, applications, and safety protocols is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients alike.
This exploration delves into the diverse types, functionalities, and clinical implications of pneumatic compression devices, highlighting their role in modern healthcare and future technological advancements.
From the basic principles of pressure gradients influencing fluid dynamics to the sophisticated engineering behind modern devices, this analysis examines the intricate details of pneumatic compression therapy. We will explore the various types of devices available, ranging from simple intermittent systems to more advanced sequential compression units, each tailored to specific clinical needs. Furthermore, we will delve into the critical role of material science in ensuring patient comfort and treatment efficacy, alongside the importance of proper maintenance and safety protocols.
Technical Specifications and Components: Pneumatic Compression Device

So, you wanna know the nitty-gritty of these pneumatic compression devices, huh? Think of it like this: it’s a high-tech hug for your legs (or arms, depending on the model). But unlike your grandma’s hug, this one’s got serious engineering behind it. Let’s dive into the nuts and bolts – or should I say, the air pumps and compression sleeves?
A pneumatic compression device is essentially a system designed to apply controlled pressure to the limbs, improving circulation and reducing swelling. It’s not rocket science, but it’s definitely more complex than your average air pump. The key components work together in a surprisingly elegant dance of pressure and relaxation.
Essential Components of a Pneumatic Compression Device
The core components are the air compressor, the control unit, and the compression sleeves themselves. The air compressor provides the pressurized air, the control unit dictates the pressure and timing, and the sleeves are the actual interface with the patient. Think of it as a carefully orchestrated symphony of pressurized air. A malfunction in any part throws the whole system off-key.
Imagine a poorly-tuned orchestra – it’s not pretty.
Materials Used in Compression Sleeves
The material of the compression sleeves is crucial for both patient comfort and treatment effectiveness. Common materials include nylon, spandex, and even neoprene. Nylon is often favored for its durability and breathability, while spandex provides elasticity and a snug fit. Neoprene, while offering excellent compression, can sometimes feel a bit too warm for extended use. The choice of material impacts how well the sleeve conforms to the limb, affecting pressure distribution and overall patient experience.
A poorly chosen material can lead to discomfort, skin irritation, or even ineffective treatment. Think of it like choosing the right pair of socks for a marathon – you wouldn’t want something scratchy and uncomfortable, right?
Function of Pressure Sensors and Control Systems
The pressure sensors and control systems are the brains of the operation. Pressure sensors constantly monitor the pressure within the compression sleeves, ensuring it stays within the prescribed range. The control unit, often featuring a digital interface, allows clinicians to adjust parameters like pressure levels, treatment duration, and inflation/deflation cycles. This precise control is essential for tailoring treatment to individual patient needs and preventing complications.
Imagine trying to bake a cake without a thermometer – you’d end up with a disaster. This is the same principle. Precise control is paramount.
Diagram of a Typical Pneumatic Compression Device
Imagine a diagram showing a simplified representation of a pneumatic compression device. At the top, we have the control unit, a small box with a digital display and buttons for adjusting settings. From the control unit, a hose leads down to the air compressor, a compact unit responsible for generating the pressurized air. Another hose connects the compressor to the compression sleeves, which are depicted wrapped around a limb.
Arrows indicate the flow of pressurized air from the compressor, through the hoses, and into the sleeves. Small icons representing pressure sensors are strategically placed within the sleeves to indicate pressure levels. A simple legend explains each component. The overall impression is one of clean lines and efficient functionality, reflecting the device’s purpose: delivering precise, controlled compression therapy.
Safety and Maintenance
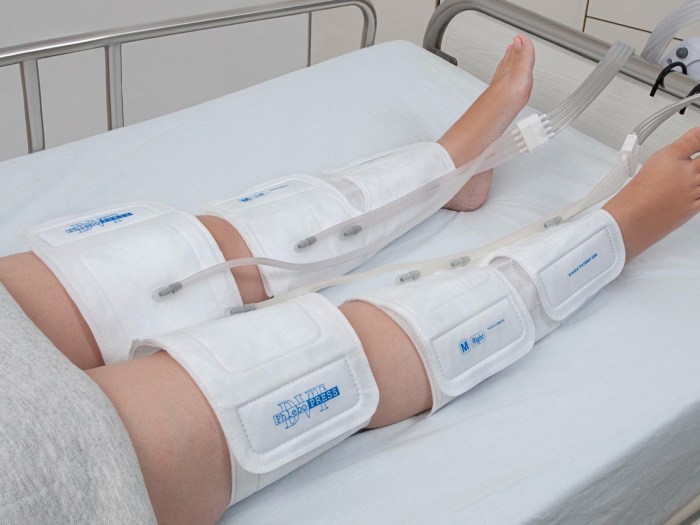
So, you’ve got yourself a snazzy pneumatic compression device. Congrats! But before you start imagining your legs looking like perfectly sculpted sausages (don’t worry, they won’t), let’s talk safety and keeping this thing running smoothly. Because nobody wants a malfunctioning machine turning their relaxation session into a scene from a low-budget horror movie.Potential Risks and Complications Associated with Pneumatic Compression DevicesThis isn’t a scary story, but there are some things to be aware of.
Improper use can lead to skin irritation, bruising, or even deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in some cases – a serious blood clot condition. Over-inflation can cause discomfort and pain, while a faulty device could lead to unexpected pressure changes, potentially causing injury. Also, always remember that these devices are not a replacement for medical advice. If you have any pre-existing conditions, consult your doctor before use.
Safe Use Guidelines
Proper fitting is key. The compression sleeves shouldn’t be too tight or too loose. Think Goldilocks – just right. Too tight, and you’ll have a throbbing limb. Too loose, and you won’t get the therapeutic benefits.
Make sure the sleeves are correctly positioned, avoiding any creases or folds that could restrict blood flow. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding pressure settings and treatment duration. Don’t exceed the recommended time or pressure levels, even if you’re feeling particularly ambitious. Remember, patience is a virtue, especially when it comes to your circulatory system.
Recommended Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is like giving your device a spa day – it keeps it happy and healthy. Check the tubing for any cracks or damage before each use. Clean the sleeves regularly with a mild detergent and allow them to air dry completely. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners. Store the device in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Periodically inspect the air compressor for any signs of wear and tear. If you notice anything unusual, consult a qualified technician before continuing to use the device. Think of it as preventative maintenance – it’s far better than dealing with a major breakdown.
Pneumatic compression devices are crucial in medical settings, offering benefits like improved circulation and edema reduction. Understanding the unique identification of these devices is paramount for tracking maintenance schedules and ensuring patient safety; this is where a robust device id profile becomes indispensable. Proper device identification is non-negotiable for effective management of pneumatic compression therapy and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues, Pneumatic compression device
Let’s say your pneumatic compression device decides to act up. Don’t panic! First, check the power supply. Is it plugged in? Is the circuit breaker tripped? Next, examine the air hoses for any kinks or blockages.
Sometimes, a simple untangling can solve the problem. If the pressure isn’t building up correctly, check the pressure gauge and ensure the settings are accurate. If the problem persists, consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or contact customer support. Remember, a little detective work can save you a lot of frustration (and potentially a hefty repair bill).
Future Trends and Innovations

So, you’ve mastered the basics of pneumatic compression devices, eh? Good. Now let’s talk about the future – because, let’s be honest, stagnant technology is about as exciting as watching paint dry (and way less colorful). We’re diving into the wild, wild west of pneumatic compression, where innovation gallops faster than a caffeinated kangaroo.Pneumatic compression therapy is on the verge of a major upgrade, moving from clunky, somewhat intimidating machines to sleek, smart devices that integrate seamlessly into our lives.
Think less hospital bed, more…well, less hospital bed. We’re talking about a revolution, people!
Smart Integration and Data Analytics
The marriage of pneumatic compression devices and smart technology is a match made in heaven (or at least, a match made in a very comfortable, well-circulated limb). Imagine a device that not only delivers compression but also monitors your progress, adjusting pressure and treatment schedules based on your individual needs. This isn’t science fiction; it’s happening now. We’re seeing devices equipped with sensors that track pressure, limb volume changes, and even skin temperature, feeding this data into sophisticated algorithms to optimize therapy.
This allows for personalized treatment plans, improved outcomes, and reduced risk of complications. Companies are developing apps that allow patients to monitor their progress, receive reminders, and even communicate directly with healthcare professionals. For example, a future scenario could see an app alerting a doctor if a patient’s swelling isn’t reducing as expected, allowing for timely intervention.
Advancements in Device Design and Functionality
The future of pneumatic compression devices isn’t just about smart features; it’s also about improved design and functionality. We’re seeing a shift towards smaller, lighter, and more portable devices. Think wearable compression sleeves that are as comfortable as your favorite pair of socks (maybe even more comfortable, because, let’s face it, who
- really* enjoys socks?). Researchers are exploring new materials and manufacturing techniques to create devices that are more durable, easier to clean, and more aesthetically pleasing. Imagine a device so stylish, you’d actually
- want* to wear it. This increased portability also means that treatment isn’t confined to a hospital or clinic; patients can receive therapy at home, at work, or even on the go. One company is already developing a device that integrates seamlessly into everyday clothing, essentially making pneumatic compression therapy invisible.
Expanding Applications Beyond Healthcare
While healthcare remains the primary focus, the potential applications of pneumatic compression technology extend far beyond. Imagine using these devices to enhance athletic performance by improving blood flow and reducing muscle soreness. Or consider their use in aerospace, where they could help astronauts combat the effects of prolonged space travel. Even in manufacturing, pneumatic compression could be used to improve worker comfort and reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
The possibilities are as limitless as a politician’s promises (almost). The technology is adaptable and has the potential to revolutionize various industries. One example is the development of specialized pneumatic compression garments for long-haul flights, designed to reduce swelling and discomfort in passengers’ legs.
In conclusion, pneumatic compression devices provide a valuable therapeutic modality with wide-ranging applications across various healthcare settings. Their effectiveness in managing edema, improving circulation, and aiding in the treatment of numerous conditions is well-established. Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to refine their design, enhance their functionality, and expand their therapeutic potential. A comprehensive understanding of their mechanisms of action, appropriate application, and potential risks is essential for maximizing their benefits and ensuring patient safety.
The future of pneumatic compression therapy holds exciting possibilities, promising further improvements in treatment efficacy and accessibility.
Key Questions Answered
What are the contraindications for using a pneumatic compression device?
Contraindications include deep vein thrombosis (DVT), acute infections in the treatment area, severe peripheral artery disease (PAD), and certain cardiac conditions. Always consult a physician before use.
How often should pneumatic compression sleeves be cleaned?
Sleeves should be cleaned after each use according to the manufacturer’s instructions, typically with mild soap and water. Air dry thoroughly before storing.
What is the typical treatment duration for pneumatic compression therapy?
Treatment duration varies depending on the condition being treated and the individual patient’s response. A physician will determine the appropriate treatment schedule.
Can pneumatic compression devices be used at home?
Yes, many pneumatic compression devices are suitable for home use, but proper training and physician oversight are usually recommended.